Projects worth more than 2.8 lakh crores inaugurated, foundation stones laid
Number of online citizen services has been increased from 18 to 58, in which there is no need to visit the RTO
Ambit of Bharat series widened; vehicles currently having regular registration mark can also be converted to BH series
Retrofitment of CNG and LPG kits allowed in BS VI vehicles
Bharat N-CAP safety rating introduced so that consumers can take informed decisions
Compensation to victims of hit and run motor accidents increased from 12,500 to 50,000 for serious accident and Rs 25,000 to Rs 2 lakh for death
Push to Green fuel & vehicles; steps taken to improve safety of electric vehicles
Construction of Amrit Sarovar along National Highways
NHAI InvIT bonds listed on Bombay Stock Exchange & National Stock Exchange
First-ever ‘Surety Bond Insurance’ for infrastructure projects launched
“Manthan” conference held in Bengaluru to discuss issues in road, transport and logistics sectors
Posted On: 04 JAN 2023 12:09PM by PIB Delhi
Major Highlights of Ministry of Road Transport and Highways 2022
INDEX
A. SALIENT FEATURES 2022
B. NATIONAL HIGHWAYS: CONSTRUCTION & ACHIEVEMENTS
C. MAJOR EVENTS OF 2022
D. PARVATMALA
E. ROAD TRANSPORT
F. ROAD SAFETY
G. LOGISTICS &ALLIED HIGHWAY INFRASTRUCTURE
H. NEW TECHNOLOGY
I. GREEN INITIATIVES
J. VEHICLE SCRAPPING POLICY
K. IAHE
L. RECORDS / RECOGNITIONS
A. SALIENT FEATURES 2022
1. Major push to Highway development
a. Inaugurations /Foundation stones laid by Hon’ble PM of projects worth more than Rs 57,020 crore
b. Inaugurations /Foundation stones laid by Hon’ble Minister RT&H of projects worth more than Rs 230,802 crore
2. Big push to connectivity:
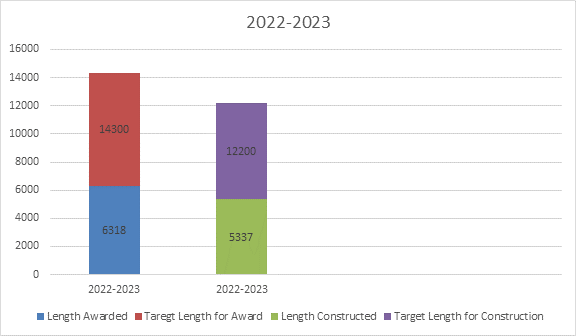
a. Award / construction: MoRTH constructed 5337 km of National Highways and awarded 6318 km of National Highways till 29th December 2022 (provisional figures).
b. Thrust on Ropeway projects under Parvatmala.
3. Major push to Logistics development in the country in line with National Logistics Policy, announced by Hon’ble PM
a. 27 Greenfield Expressways being developed across the country
b. First MMLP in PPP mode awarded
c. Bid for 3 more MMLPs in process
4. Number of online citizen services has been increased from 18 to 58, in which there is no need to visit the RTO
5. Ambit of Bharat series widened; vehicles currently having regular registration mark can also be converted to BH series
6. Retrofitment of CNG and LPG kits allowed in BS VI vehicles
7. Bharat N-CAP safety rating introduced so that consumers can take informed decisions.
8. Compensation to victims of hit and run motor accidents increased from 12,500 to 50,000 for serious accident and Rs 25,000 to Rs 2 lakh for death
9. Push to Green fuel & vehicles; steps taken to improve safety of electric vehicles
10. Construction of Amrit Sarovar along National Highways
11. NHAI InvIT bonds listed on Bombay Stock Exchange & National Stock Exchange
12. “Manthan” conference held in Bengaluru to discuss issues in road, transport and logistics sectors
B. NATIONAL HIGHWAYS: CONSTRUCTION & ACHIEVEMENTS
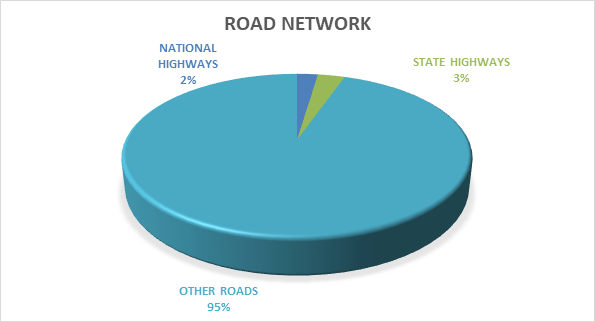
1. Road Network in the Country: India has about 63.73 lakh km of road network, which is the second largest in the world.
The length of various categories of roads is as under:
- National Highways: 1,44,634 km
- State Highways: 1,86,908 km
- Other Roads: 59,02,539 km
National Highways play a very important role in the economic and social development of the country by enabling efficient movement of freight and passengers and improving access to market. MoRTH and its implementing agencies have implemented multiple initiatives in last 8 years to augment the capacity of the National Highway infrastructure in India.
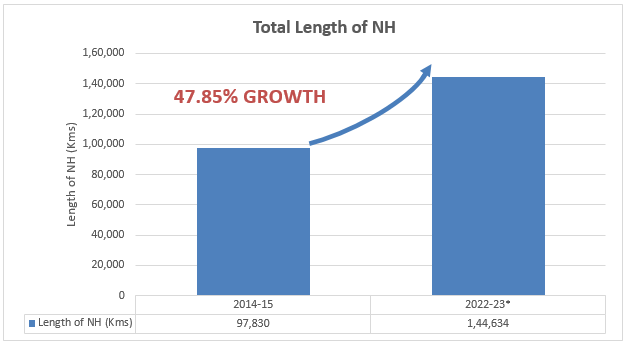
As on 30 November 2022, the total length of National Highways in the country was 1,44,634 km.
As on 30 November, 2022
Award / construction: MoRTH constructed 5337 km of National Highways and awarded 6318 km of National Highways till 29th December, 2022 (Provisional figures).
| Sr. No. | Year | Length (in km) |
| 1 | 2014-15 | 97,830 |
| 2 | 2015-16 | 1,01,010 |
| 3 | 2016-17 | 1,14,158 |
| 4 | 2017-18 | 1,26,500 |
| 5 | 2018-19 | 1,32,500 |
| 6 | 2019-20 | 1,32,995 |
| 7 | 2020-21 | 1,38,376 |
| 8 | 2021-22 | 1,41,345 |
| 9 | 2022-23 | 1,44,634* |
(* Till 30 November 2022)
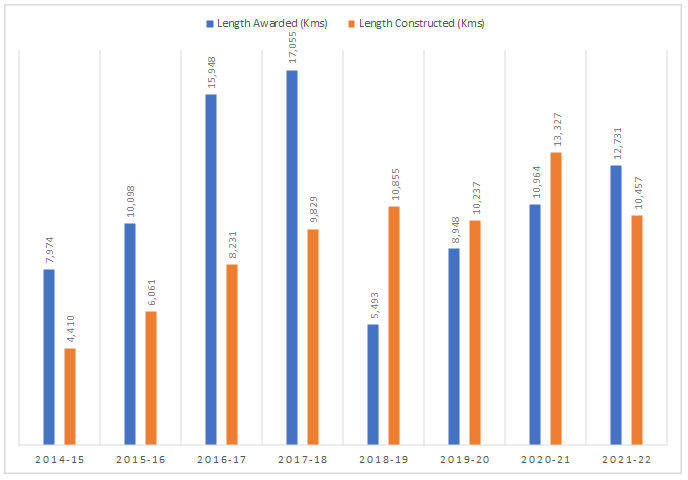
The pace of National Highways (NH) construction has increased consistently between 2014-15 and 2021-22 due to the systematic push through corridor-based National Highway development approach. In 2014-15, the pace of NH construction was about 12 km/ day which increased to about 29 km/ day in 2021-22.
| Sr. No. | Year | Award(in km) | Construction (in km) | Construction (in km / day) | |
| 1 | 2014-15 | 7,974 | 4,410 | 12.1 | |
| 2 | 2015-16 | 10,098 | 6,061 | 16.6 | |
| 3 | 2016-17 | 15,948 | 8,231 | 22.6 | |
| 4 | 2017-18 | 17,055 | 9,829 | 26.9 | |
| 5 | 2018-19 | 5,493 | 10,855 | 29.7 | |
| 6 | 2019-20 | 8,948 | 10,237 | 28.1 | |
| 7 | 2020-21 | 10,964 | 13,327 | 36.5 | |
| 8 | 2021-22 | 12,731 | 10,457 | 28.6 | |
| 9 | 2022-23 | 6318 (till 29 Dec 2022) | 5337 (till 29 Dec 2022) | ||
(Length in Kms)
2. Bharatmala Pariyojana: The Bharatmala Pariyojana was launched with the primary focus on optimizing the efficiency of the movement of goods and people across the country. The Phase I of the Bharatmala Pariyojana approved in October 2017, focuses on bridging critical infrastructure gaps through development of 34,800 km of National Highways. The Pariyojana emphasized on a “corridor based National Highway development” to ensure infrastructure symmetry and consistent road user experience. The key components of the Pariyojana are Economic Corridors development, Inter-corridor and feeder routes development, National Corridors Efficiency Improvement, Border and International Connectivity Roads, Coastal and Port Connectivity Roads and Expressways.
As part of Phase-I of the programme, 27 Greenfield corridors are planned with an overall length of 9,000+ kms. As a part of Bharatmala Pariyojana, India’s largest expressway, i.e.,1,386 km long Delhi-Mumbai Expressway is being developed and some sections such as Delhi – Dausa (Jaipur), Vadodara – Ankleshwar sections of the Expressway are nearing completion. Other key corridors which have already been completed/nearing completion are Ambala – Kotputli Corridor & Amritsar – Jamnagar Corridor.
In Bharatmala Pariyojana, 60% projects on Hybrid Annuity Mode, 10% projects on BOT (Toll) Mode and 30% projects on EPC mode have been envisaged respectively.
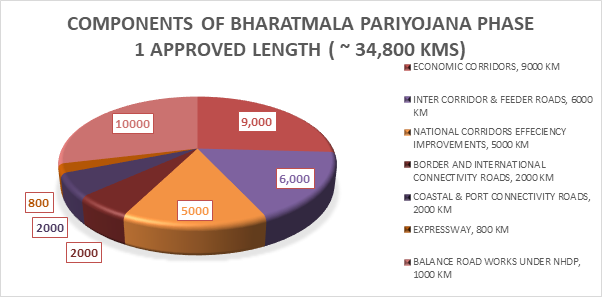
(Figures in kms)
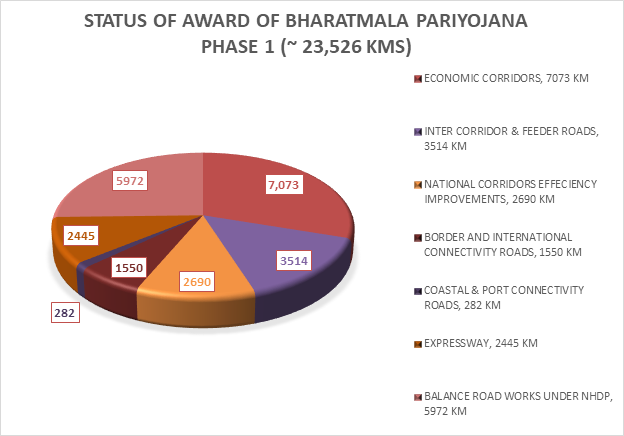
(Figures in kms)
Out of the ~24,800 km approved under Bharatmala Pariyojana Phase-I, total length of 17,555 km have been awarded. Similarly, out of the residual NHDP component 10,000 km to be completed Bharatmala Phase-I, a total length of 5,972 km have been awarded.
3. Tollable Highways added in FY 2022-23
| Sr. No. | Parameter & Unit | 2022-23 |
| 1 | Highway Length Tolled (km) | 2782* |
| 2 | Toll Collection (Rs Crore) | 15958.13** |
| *Till November 2022, ** Till November 2022 |
4. Relief for Contractors/Developers of the Road Sector in view of the COVID-19 pandemic: The Ministry provided/extended the relief measures in view of the Covid-19 pandemic.
(i) Extension of relaxation in Schedule H/G till 31st March 2023 to improve the liquidity of funds available with the Contractors and Concessionaire.
(ii) Arrangement regarding direct payment to approved Sub-Contractor through Escrow Account may be continued till 31st March 2023 or the completion of the work by the Sub-Contractor, whichever is earlier.
(iii) Reduction of Performance Security/release of retention money: The Ministry has already decided to reduce Performance Security from existing 5–10 % to 3% of the value of the contract for all existing contracts (excluding the contracts under dispute wherein arbitration/court proceedings have already been started or are completed). All tenders /contracts issued/ concluded till 31.03.2023 should also have the provision of reduced performance security.
5. Reinstatement of provision of Earnest Money Deposit (EMD) in bids for highway projects: On the expiry of applicability of the Department of Expenditure’s O.M. No.9/4/2020-PPD dated 12.11.2020 regarding bid security on 31.12.2021, provisions of Rule 170 of GFR, 2017, which existed before the issue of the aforesaid DoE OM, have been reinstated allowing the provision of Bid Security or Bid Securing Declaration in place of Bid Security for all modes of road construction under PPP including EPC.
6. Asset Monetization:
(i) Bids invited for 4 Projects (382 km) for a concession period of 20 years under 3 ToT Bundles in August 2021 (Extended Bid Due date 27.01.2022 for TOT Bundle 6 & 7 and 31.01.2022 for TOT Bundle 8).
(ii) National Highways Infra Trust (NHAI InvIT) Bonds: NHAI InvIT bonds were successfully listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange & National Stock Exchange on 28th Oct 2022 in the presence of RT&H Minister Shri Nitin Gadkari NHIT raised a sum of Rs 1,500 crore through an issue of secured, rated, listed, redeemable, non-convertible debentures securities (“Bonds”) with a long-dated maturity of 25 years. The Bonds were issued with a coupon of 7.9% payable half yearly, which works out to 8.05% interest for the year. The minimum investment amount was kept low at Rs 10,000/- to encourage the participation of retail investors. NHIT Bonds received enormous interest from multiple investor classes and were called for early closure on the second day due to over-subscription.
7. Amrit Sarovar: Under the aegis of “Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav”, “Amrit Sarovar Abhiyan”, an initiative to develop and rejuvenate ponds has been taken. The soil, silt and other things extracted from these reservoirs are being used for construction of National Highway work.
8. Surety Bonds launched: Union RT&H Minister Shri Nitin Gadkari launched first-ever ‘Surety Bond Insurance’ for infrastructure projects. With this new instrument of Surety Bonds, the availability of both liquidity and capacity will definitely be boosted; such products stand to strengthen the infrastructure sector.
C. MAJOR EVENTS OF 2022
(i) INAUGURATIONS / LAYING OF FOUNDATION STONE BY PRIME MINISTER SHRI NARENDRA MODI
1. Inaugurated of Banihal-Qazigund road tunnel (Rs 3100 crore); Foundation stone of 3 road packages of Delhi-Amritsar-Katra package (Rs 7500 crore) (24 April)
2. Laid the foundation stone of six projects, being built at a cost of over Rs. 28,540 crore. The 262 Km long Bengaluru – Chennai Expressway will be built at a cost of over Rs. 14,870 crore. The 4 Lane double decker elevated road connecting Chennai Port to Maduravoyal (NH-4), of about 21 Km in length, will be built at a cost of over Rs 5850 crore. It will facilitate round the clock approach of goods vehicles to Chennai port. The 94 km long 4 lane Neraluru to Dharmapuri section of NH-844 and 31 km long 2 lane with paved shoulders of Meensurutti to Chidambaram section of NH-227, being built at a cost of around Rs 3870 crore and Rs 720 respectively, will help provide seamless connectivity in the region. (26 May)
3. Laid the foundation stone of MMLP Chennai (26 May)
4. Laid the foundation stone of two sections of the Bengaluru Ring Road project, to be developed at a cost of more than ₹2,280 crore. (20 June)
5. Laid the foundation stone of MMLP, which is being developed at Muddalinganahalli, about 40 km from Bengaluru.
6. Inaugurated and laid the foundation stone of multiple road projects worth more than Rs. 10,000 crores. The projects include six laning of Gorhar to Barwada section of NH-2; widening of Rajganj – Chas upto West Bengal border section of NH-32 among others. The major projects include four laning of Mirzachowki- Farakka section of NH-80; four laning of Hariharganj to Parwa More section of NH-98; four laning of Palma to Gumla section of NH-23; Elevated corridor of Kutchery Chowk to Piska More section of NH-75 among others. (12 July)
7. Laid the foundation of road and Ropeway projects worth more than Rs 3,400 crores in Mana, Uttarakhand. The ropeway in Kedarnath will be around 9.7 Km in length and will connect Gaurikund to Kedarnath. The Hemkund ropeway will connect Govindghat to Hemkund Sahib. It will be around 12.4 Km in length. This ropeway will also connect Ghangaria, which is the gateway to Valley of Flowers National Park. The two road widening projects – from Mana to Mana Pass (NH07) and from Joshimath to Malari (NH107B) – will be another step towards providing last-mile all-weather road connectivity to our border areas. (21 October)
8. Laid the foundation stone of AP section of six-lane Greenfield Raipur – Visakhapatnam Economic Corridor and a dedicated Port Road from Convent Junction to Sheela Nagar Junction (12 November)
9. Inaugurated widening project of Agartala Bypass (Khayerpur – Amtali) NH 08 (17 December)
10. Laid the foundation stone of various road projects worth over Rs. 2200 crore, namely Medak-Siddipet-Elkathurthy section of NH-765DG; Bodhan-Basar-Bhainsa section of NH-161BB; Sironcha to Mahadevpur Section of NH-353C in Telangana. (12 November)
(ii) INAUGURATIONS / LAYING OF FOUNDATION STONE BY MINISTER RT&H SHRI NITIN GADKARI
1. Inaugurated and laid foundation stone for 821 km of National Highways worth Rs 26778 crore in Uttar Pradesh. He also inaugurated and laid foundation stones in Kanpur for 8 National Highway projects worth Rs 14,199 Crore, in Lucknow for 16 National Highway projects worth Rs 7409 Crore and in Shringverpur Dham, Prayagraj for 4 National Highway projects worth Rs 5169 Crore. (5 June)
2. Inaugurated and laid foundation stones for 572 km of National Highway(NH) projects at a cost of Rs.12981 crore in Kaushambi, Ayodhya and Basti in Uttar Pradesh. He also Inaugurated and laid foundation Stone of 6 NH Projects worth Rs 2659 Crore in Kaushambi. In Ayodhya he laid foundation stone of 6 NH Projects worth Rs 8,698 Crore and in Basti the Minister inaugurated and laid foundation stone of 3 NH Projects worth Rs 1,624 crore. The construction of 84 Kosi Parikrama Marg in Ayodhya will facilitate the devotees and encourage religious tourism. With the construction of Ayodhya Ring Road, the traffic congestion issues will be resolved. Important pilgrimage sites Prayagraj Chitrakoot Kaushambi and Shringverpur Dham will get connected with the construction of Lord Shri Ram Van Gaman Marg. (6 January)
3. Virtually laid Foundation Stone of 10 National Highway Projects for 336 kms worth Rs 14169 Crore in Mathura in Uttar Pradesh. With the construction of a bypass connecting Agra Inner Ring Road and Yamuna Expressway, the city of Agra will get rid of traffic jams. (7 January)
4. Inaugurated 14.5 km long Rail-cum-Road-bridge over Ganga River approach project on NH 333B in Munger, Bihar at a cost of Rs.696 crore. (11 February)
5. Inaugurated and laid Foundation Stone of 51 National Highway Projects of total length 1380 Km with an investment of Rs 21,559 Crore in Vijaywada, Andhra Pradesh. (17 February)
6. Laid foundation stones for 11 National Highways projects with total length of 534 km worth Rs 5722 crore in Madhya Pradesh. (24 February)
7. Inaugurated and laid foundation stone of 46 National Highway Projects with investment of Rs 19,930 crore in Karnataka. (28 February)
8. Inaugurated 19 National Highway projects worth Rs 1407 crore in Haryana and Rajasthan. (19 March)
9. Dedicated to the nation two Highway Projects worth ₹ 2,334 Cr in Sangli, Maharashtra. The total length of two section of Highway Projects dedicated today is 96.78 km. (26 March)
10. Inaugurated and laid foundation stone for National Highway projects worth Rs. 4,135.91 crore. The development work comprises dedication of Rs. 3,500 crore JNPT Port Road Connectivity Project to the nation and ground-breaking ceremony for work on National Highway No. 48, Mumbai-Pune Expressway, Kalamboli Junction Improvement Project and the eastern entrance of proposed Navi Mumbai International Airport. (3 April)
11. Inaugurated 5 National Highway projects of 297 km length costing Rs 2,872 crore in Sonepat, Haryana. (4 April)
12. Inaugurated and laid foundation stone of 33 National Highway projects in Raipur, Chhattisgarh worth Rs 9,240 crore. (21 April)
13. Inaugurated and laid foundation stones for 16 National highways projects worth Rs 2,460 crore in Jalgaon, Maharashtra. Inaugurated and laid foundation stones for 2 National highways projects worth Rs 1,791.46 crore in Dhule, Maharashtra. (22 April)
14. Inaugurated 7 National Highway Projects worth Rs.5569 crores in Aurangabad, Maharashtra. (24 April)
15. Inaugurated 10 National Highway projects of 292 km worth Rs.8,181 crores in Solapur, Maharashtra. (25 April)
16. Inaugurated 12 National Highway Projects of total length of 460 Km worth Rs 8000 crore and 7 CRIF Projects in Hyderabad. in presence of MoS Gen V. K. Singh. (29 April)
17. Inaugurated and laid foundation stones of 15 National Highway projects in Patna and Hajipur in Bihar with a total cost of Rs.13,585 crore. (7 June)
18. Inaugurated and laid foundation stone of 9 NH projects of 243 km length worth Rs 1357 crore in Rajasthan. (27 June)
19. Inaugurated the Savner-Dhapewada-Goundkhairi section of National Highway 547-E with a length of 28.88 km and a cost of Rs 720 crore in Nagpur. (24 July)
20. Inaugurated and laid foundation stone of 6 National Highway projects of 119 Km worth Rs. 2300 crore in Indore, Madhya Pradesh. (1 August)
21. Inaugurated and laid the foundation stone of 7 National Highway projects costing Rs 1,128 crore and total length of 222 km. (15 September)
22. Laid the foundation stones for 8 National Highway Projects worth Rs 3000 crore in Rajamahendravaram, Andhra Pradesh. (22 September)
23. Inaugurated and laid the foundation stone of 8 National Highway projects worth Rs 4054 crore and 214 km length in Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh; inaugurated 5 National Highway projects of total length 329 km in Mandla, Madhya Pradesh at a cost of Rs 1261 crore. (7 November)
24. Inaugurated two National Highway projects worth Rs 3,390 crore in Buxar, Bihar; inaugurated 1.5 km long 2-lane elevated R.C.C. bridge near Panduka on Son river in Rohtas, Bihar at a cost of Rs 210 crore. (14 November)
25. Inaugurated 2 NH projects worth Rs 1082 Crore at Raiganj,West Bengal; inaugurated and laid the foundation stone for 4 NH projects worth Rs. 5351 Crore in West Medinipur, West Bengal; inaugurated and laid the foundation stone of 3 NH projects worth Rs. 1206 Crore in Siliguri, West Bengal. (17 November)
26. Inaugurated the construction of 3.8 km long 4-lane elevated structure flyover at Ahmednagar, Maharashtra on National Highway-61 at a cost of Rs 331.17 crore. (19 November)
27. Inaugurated 7 National Highway projects worth Rs 2,444 crore with total length of 204 km in Rewa, Madhya Pradesh. (10 December)
28. Inaugurated and laid foundation stone of 8 National Highway projects of 226 km length worth Rs 1800 crore at Igatpuri, Nashik, Maharashtra. (18 December)
(iii) OTHER EVENTS
1. MANTHAN: A two-day conference cum public EXPO “Manthan” was organised by MoRTH on 8-9 September with an aim to anchor discussions across multiple issues and opportunities in the roads, transport and logistics sector and engage with the States, UTs and other key stakeholders from the industry for sharing of best practices, policy support, and capacity development. The theme of Manthan was “IDEAS TO ACTION: Towards a smart, sustainable, road infra, mobility and logistics ecosystem”. Several state ministers holding portfolios of the ministries of PWD, Transport and Industries and senior government officials from these ministries participated in the conference. In addition, senior industry leaders and experts also joined the event. Apart from these, senior officials from MoRTH and NHAI, policy planners, experts, corporate leaders and technocrats, amongst others, also attended the deliberations during the event. On this occasion, three short films, featuring Bollywood actor Akshay Kumar, on road safety, were also released.
2. PM-GATI SHAKTI SOUTH ZONE CONFERENCE: Union Road Transport and Highways Minister Shri Nitin Gadkari inaugurated a virtual Conference on “PM-Gati Shakti” for the South Zone, organized by MoRTH. He said communication needs to be enhanced between State and Centre. State/UTs, which participated in the event, were Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep, Maharashtra, Puducherry, Tamil Nadu and Telangana.
3. NATIONAL HIGHWAYS EXCELLENCE AWARDS: The “National Highways Excellence Awards (NHEA) 2021” ceremony was organized by MoRTH at Vigyan Bhavan in New Delhi on 28 June. The theme of the awards was “Innovation and Excellence in Road Construction”. During the ceremony, awards were presented to the concessionaire/contractors working exceptionally well in the construction, operations & maintenance, innovation, greenery, tolling stages of highway development as well as in the arena of road safety for the 2021 award cycle. As many as 122 nominations were received, out of which 13 were selected for the awards. A conference “Arteries of New India: Highways and Road to the Future (Innovation and Excellence in Road Construction) was also organized on the same day.
4. SPECIAL CAMPAIGN 2.0: As part of the “Special Campaign 2.0”, MoRTH undertook various activities all over the country, including “Swachhta Abhiyan” (cleanliness drive) at various toll plazas, disposing pending files, weeding out scrap and making roads pothole-free. The activities took place at HQ and field offices of MoRTH, NHAI, NHIDCL, IRC and IAHE, from 2 – 31 October. As part of the campaign, 667 out of a target of 694 MP references, 1042 out of 1,049 Public Grievances, 15 out of 16 PMO references, 35 out of 59 Parliamentary assurances, 28 out of 28 State Government references were disposed of while 12,612 physical files, which were identified for weeding, were weeded out. Cleanliness campaigns were carried out at 2,466 locations, which include toll plazas, Regional Offices & PIU/PMUs of MoRTH/NHAI/NHIDCL. The Ministry earned Rs 7.09 lakh by disposing scrap during the campaign. As much as 1,936 sq ft space was freed after files were weeded out and scraps were disposed.
D. PARVATMALA
1. Convenient and preferred mode of transportation: Ropeways have emerged as a convenient, safe and preferred mode of transportation to provide both, first as well as last mile connectivity to such hilly & inaccessible areas or to help de-congest urban congestion areas. In this backdrop, the Centre is giving a major push to ropeway development in the country. The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRT&H) is responsible for the development of highways and regulating the road transport sector across the country. However, an amendment in the Government of India (Allocation of Business) Rules 1961 in February 2021, enabled MoRT&H to oversee and undertake the development of Ropeways and Alternate Mobility Solutions in the country.
2. PM lays foundation stone of 2 new ropeway projects: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone of two new ropeway projects connecting Gaurikund to Kedarnath and Govindghat to Hemkund Sahib in Uttarakhand. The ropeway in Kedarnath will be around 9.7 Km in length and will connect Gaurikund to Kedarnath, thereby reducing the travel time between the two places from 6-7 hours at present to merely 30 mins. The Hemkund ropeway will connect Govindghat to Hemkund Sahib. It will be around 12.4 Km in length and will reduce the travel time from more than a day to only about 45 mins. This ropeway will also connect Ghangaria, which is the gateway to Valley of Flowers National Park.
3. MoU for ropeways in Himachal Pradesh: Under the leadership of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi to improve the First and Last Mile Connectivity through Ropeways, Union Minister for Road transport and Highways Shri Nitin Gadkari along with Chief Minister of Himachal Pradesh Shri Jai Ram Thakur, MoS Shri V. K. Singh witnessed the signing of MoU between NHLML(National Highways Logistics Management Limited) and State Government of Himachal Pradesh for construction of Ropeways in Himachal Pradesh under the ambitious Parvatmala Yojana.
4. MoU for ropeways in MP: An MoU was signed between Madhya Pradesh Government and NHAI for construction of ropeways at 14 selected places in the state.
E. ROAD TRANSPORT
Road transport is the dominant mode of transport in India, both in terms of traffic share and contribution to the national economy. Apart from facilitating the movement of goods and passengers, road transport plays a key role in promoting equitable socio-economic development across regions of the country. It also plays a vital role in social and economic integration and development of the country. Easy accessibility, flexibility of operations, door-to-door service and reliability have earned road transport a greater significance in both passenger and freight traffic vis-à-vis other modes of transport.
Strengthening ITS in Public Transport System: The Ministry has revamped its previous ITS Scheme and issued guidelines on June 23rd, 2022, to continue the previous scheme. This will provide additional financial support to STUs to equip themselves with advanced ITS technologies, improved bus services, operations, performance, and customer conveniences. The Scheme provides support of hardware and software components for Fleet Management System, Electronic Ticketing & Fare Collection System (including NCMC) and Passenger Information & Feedback System.
So far, proposals amounting to over Rs 200 crores have been received in the Ministry from several STUs such as TSRTC, KSRTC, GSRTC, BEST, Ahmedabad Jalmarg Ltd., Bhopal City Link Ltd., Kerala SRTC etc. These proposals are under consideration of this Ministry and several of them are already in advanced stages of appraisal.
(i) CITIZEN-CENTRIC MEASURE
1. Facilitation in availing transport related services using Aadhar: MoRTH issued a notification increasing 18 citizen-centric services to 58 services related to driving license, conductor license, vehicle registration, permit, transfer of ownership etc, completely online, eliminating the need to visit the RTO. These services can be availed with the help of Aadhaar authentication, on voluntary basis. Providing such services in a contactless and faceless manner will go a long way in saving time of citizens while easing their compliance burden. Consequently, the footfall at the RTOs is likely to significantly reduce, which would lead to greater efficiency in their functioning.
| 1. Application for Learner License (LL).2. Change of Address in Learner License.3. Change of Name in Learner License.4. Change of Photo and Signature in Learner License.5. Issue of Duplicate Learner License.6. Learner License Extract provisioning.7. Issue of Duplicate Driving License (DL)8. Renewal of Driving License for which test of competence to drive is not required.9. Replacement of Driving License.10. Application for registration for driver training from Accredited Driver Training Centre and requirementof passing certificate to be sent to concerned Regional Transport Office (RTO) for issuance of DrivingLicense (DL).11. Change of Address in Driving License.12. Change of Name in Driving License.13. Change of Biometrics in Driving License.14. Change of Date of Birth in Driving License.15. Change of Photo and Signature in Driving License.16. Driving License Extract provisioning.17. Issue of International Driving Permit.18. Surrender of Class of Vehicle from License.19. Endorsement to Drive Hazardous Material.20. Endorsement to Drive in Hill Region.21. Issue of Driving License for Defence.22. Additional endorsement on Driving license (AEDL) for Defence Driving License Holder.23. Issue of Public Service Vehicle (PSV) Badge to Driver.24. Issue of Duplicate Public Service Vehicle (PSV) Badge.25. Temporary Public Service Vehicle (PSV) Badge to Driver.26. Renewal of Conductor License.27. Issue of Duplicate Conductor License.28. Conductor License Extract provisioning.29. Issue of Temporary Conductor License. | 30. Change of Address in Conductor License.31. Change of Biometrics in Conductor License.32. Change of Name in Conductor License.33. Application for Temporary Registration of motor vehicle.34. Application for Registration of motor vehicle with fully built body.35. Application for issue of duplicate Certificate of Registration (RC).36. Deposit of Registration Certificate fees.37. Application for Grant of No Objection Certificate (NOC) for Certificate of Registration.38. Change in Address in Certificate of Registration.39. View Registration Certificate (RC) particulars against fee.40. Retention of Registration Number.41. Notice of Transfer of Ownership of motor vehicle.42. Application for Transfer of Ownership of motor vehicle.43. Payment of additional Life Time Tax (Transfer of ownership Case).44. Endorsement of hire-purchase agreement.45. Termination of hire-purchase agreement.46. Issue or Renewal of Trade Certificate.47. Issue of Fresh Permit.48. Issue of Duplicate Permit.49. Permit Non-Use Intimation.50. Permanent Surrender of Permit.51. Transfer of Permit.52. Transfer of Permit (Death Case).53. Renewal of Permit.54. Renewal of Permit Authorisation.55. Application for Special Permit.56. Application for Temporary Permit.57. Update Mobile Number in record for transport services.58. Issue of Duplicate Fitness certificate. |
2. Ambit of Bharat series expanded: MoRTH notified amendments in the rules governing Bharat (BH) series registration mark. MoRTH had introduced BH series registration mark in 2021. Over the course of implementation of these rules, several representations have been received towards strengthening the BH series ecosystem. In an endeavour to further improve as well as widen the scope of BH series implementation, MoRTH has notified new rules with new key features.
3. Accredited Driver Training Centres (ADTC) Rules: Ministry of Road Transport & Highways (MoRTH) notified amendment to the rules related to Accredited Driver Training Centres (ADTC) notified. Over the course of the implementation of referred rules, certain issues were identified by this Ministry as well as other stakeholders. New rules will further streamline the functioning of ADTCs with many new features.
4. Movement of Non-Transport (Personal) foreign vehicles in India: MoRTH issued the Motor Vehicles Non Transport Vehicles Visiting India Rules, 2022. These rules formalize the movement of Non-Transport (Personal) vehicles registered in other countries when entering or plying in the territory of India.
5. Standardisation of International Driving Permit (IDP): The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways issued a notification on 26 August 2022 for greater facilitation of citizens in the issue of International Driving Permit (IDP) across the country. India, being a signatory to Convention on International Road Traffic of 1949 (Geneva Convention), is required to issue IDP as provided under this Convention, for the acceptance of the same on reciprocal basis with other countries.
6. Vehicle Location Tracking Device for vehicle carrying any dangerous or hazardous goods: The Ministry has mandated that every vehicle of categories N2 and N3, manufactured on and after the 1st Day of September, 2022, in the case of new models, and 1st day of January, 2023, in the case of existing models, carrying dangerous or hazardous goods, shall be fitted with a vehicle tracking system device as per AIS 140.
7. Triple deck to transport two wheelers: The Ministry issued a notification on 25th February 2022 to amend Rule 93 of the Central Motor Vehicles Rules 1989, whereby rigid vehicles and trailers can have a maximum of three decks to transport two wheelers, with the load body not projecting over the driver’s cabin. This will enhance the carriage capacity of two wheelers by 40-50%.
8. Type approval of Cash Van: MoRTH issued a notification on 23rd February, 2022, whereby Cash Vans shall comply with the minimum requirements as stated in Automotive Industry Standard-163:2020, as amended from time to time, till the corresponding BIS specifications are notified under the Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 2016(11 of 2016).
9. Deferment of the date of implementation for Emission Norms (TREM IV) for tractors, combine harvesters and power tiller:-Accordingly, this Ministry, vide GSR 413(E) dated 2nd June, 2022 has deferred the date of implementation of Emission Norms (TREM IV) for tractors, combine harvesters and power tiller from 1st April, 2022 to 1st October, 2022 i.e by six months. It has been further extended to 1st January, 2023 vide GSR 850(E) dated 24th November, 2022
10. Constant Speed Fuel Consumption Test for M and N categories: This Ministry vide S.O. 4144(E) dated 2nd September, 2022 has notified the BIS standard (IS: 11921: 2020) for the Constant Speed Fuel Consumption Test for M and N categories of vehicles, except tippers, having GVW (Gross Vehicle Weight) greater than 3.5 tonnes.
11. Trade Certificate regime: Ministry of Road Transport & Highways published a draft notification dated 5th May 2022 regarding amendments in certain provisions of the Central Motor Vehicles Rules 1989 pertaining to the Trade Certificate. It is proposed that an agency can apply for a Trade Certificate and Trade Registration Marks electronically for multiple types of vehicles in a single application on the Vahan portal, without the need to visit the RTO.
12. Motor Vehicles (Third Party Insurance Base Premium and Liability), Rules 2022: The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, in consultation with the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India, has published Motor Vehicles (Third Party Insurance Base Premium and Liability) Rules, 2022 vide notification dated 25.05.2022. The rules shall come into force on 1st June, 2022. In the said rules, base premium for third party insurance for unlimited liability has been notified for various classes of vehicles.
13. Retrofitment in BS VI Vehicles: Ministry of Road Transport and Highways vide G.S.R. 625(E) dated 11th August, 2022 notified regarding retrofitment of CNG and LPG kit on BS (Bharat Stage)-VI gasoline vehicles and replacement of diesel engines with CNG/LPG engines in case of BS-VI vehicles, less than 3.5 tonnes. As of now, retrofitment of CNG and LPG kits is permissible in motor vehicles complying with BS IV emission norms.
14. Implementation of Section 44 of the Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019: The Ministry, vide S.O. 691 (E) dated 15th February, 2022, notified the implementation of Section 44 of the Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019. It mandates that every person, above four years of age, driving or riding or being carried on a motorcycle of any class or description shall, while in a public place, wear protective headgear conforming to such standards, as may be prescribed by the Central Government.
15. Specific exemptions for Armoured Vehicles from the provisions under the Central Motor Vehicles Rules, 1989: The Ministry vide G.S.R. 863(E) dated 1st December, 2022 notified to insert a new rule 125L in CMVR (Central Motor Vehicles Rules), 1989 whereby it has been prescribed that Specific exemptions for Armoured Vehicles from the notified provisions under the Central Motor Vehicles Rules, 1989, shall be in accordance with AIS-194:2022, as amended from time to time.
16. Fuel efficiency Norms for Light, medium and heavy motor vehicles: This Ministry vide G.S.R. 844(E) dated 22nd November, 2022 has amended Rule 115G of Central Motor Vehicle Rules (CMVR) 1989 to include compliance to Fuel Consumption Norms for light, medium and heavy duty motor vehicles of various categories, excluding Tippers, manufactured or imported to India.
17. Ease of doing business and transparency in the sale and purchase of registered vehicles: The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) has issued a draft notification G.S.R 693(E) on 12 September 2022 to promote ease of doing business and transparency in the sale and purchase of registered vehicles through dealers.
18. All India Tourist Vehicle (Authorisation or Permit) Rules, 2021: The Ministry issued a draft notification on 11 November 2022 to supersede the All India Tourist Vehicle (Authorisation or Permit) Rules, 2021. The rules notified in 2021 provided a significant boost to the tourism sector in India by streamlining and simplifying the permit regime for tourist vehicles.
(ii) INITIATIVES FOR DIVYANGJANS
1. Accessible India Campaign (Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan): The Accessible India Campaign was launched by Hon’ble Prime Minister for creating universal accessibility for persons with Disabilities in Built Environment, Transport, and Information & Communication Technology (ICT) ecosystem. The Campaign is based on the principles of the Social Model of Disability, which mentions that disability is caused by the way society is organized, and is not based on the person’s limitations and impairments. Physical, social, structural and attitudinal barriers prevent people with Disabilities (Divyangjan) from participating equally in socio-cultural and economic activities.
2. Accessibility guidelines: The Ministry issued the Accessibility Guidelines for Bus terminals and Bus Stops on 29.08.2022 which cover the planning and design aspects of areas in bus ports/bus terminals and bus stops, so that these areas can be made accessible to all. Special emphasis has been laid on ensuring ease of access for the use of these facilities by end users.
In order to ensure widespread use of these guidelines in the transport infrastructure across the Country, through letter dated 05.09.2022, Executive Director of the Association of State Road Transport Undertakings (ASRTU) was also requested to distribute copies of the guidelines to the member STUs of ASRTU. In this regard, data has been compiled in respect of 62 STUs by ASRTU vide their letter dated 30th October, 2022. It was brought out that total number of operational buses is 146081, the number of buses involved in intercity operations is 101908 and in urban operations this is 44173.
F. ROAD SAFETY
(i) PREVENTIVE MEASURES
1. Regulations for Bharat New Car Assessment Programme: MoRTH issued a draft notification on 24 June, whereby it is proposed to insert a new rule 126E in CMVR (Central Motor Vehicles Rules), 1989 regarding the Bharat New Car Assessment Program (BNCAP). Bharat NCAP rating will provide consumers an indication of the level of protection offered to the occupants.
2. Rules regarding side/side torso air bags and side curtain/tube air bags: The Ministry, vide notification dated 30th September, 2022, has proposed to insert new sub-rule 9B in rule 125 of the CMVR, 1989, to introduce the provision for the fitment of side/side torso airbags and side curtain/tube airbags in M1 category vehicles. The requirement for such airbags shall be verified with compliance to AIS-099 as amended from time to time. The implementation of the said rule is proposed to be from 01st October, 2023.
3. Seat belt: The Ministry vide notification dated 30th September 2022 issued a draft notification, wherein it was proposed that all front facing seats in vehicles of M1 category (i.e, a motor vehicle used for carriage of passengers, comprising not more than 8 seats, in addition to the driver’s seat), manufactured on and after 01st April, 2023, be provided with three point seat belt.
4. Norms for Tyre Rolling Resistance, Wet Grip and Rolling Sound: MoRTH issued a notification on 28th June, amending rule 95 of the Central Motor Vehicles Rules 1989. It mandates requirements of Rolling resistance, Wet Grip and Rolling Sound Emissions for tyres falling under classes C1(passenger cars) , C2 ( light truck) and C3 (truck and bus), as defined in the Automotive Industry Standard 142:2019. The said tyres shall meet the Wet grip requirements and Stage 2 limits of Rolling Resistance and Rolling Sound Emissions, as specified in this AIS.
5. Safety and Security of Women Passengers (Projects under Nirbhaya Framework): The Government of India has set up a dedicated fund under the Nirbhaya Framework being administered by the Department of Economic Affairs, M/o Finance. Standalone projects from the Government of Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation and Bangalore Metropolitan Transport Corporation have been approved under the Nirbhaya Fund Scheme to augment safety and security of women in public road transport, which are under different stages of execution.
6. Safety measures for children below four years of age riding or being carried on a motor cycle: The Ministry amended Rule 138 of CMVR, 1989 and prescribed norms related to safety measures for children below four years of age, riding or being carried on a motor cycle. This has been notified under Section 129 of the Motor Vehicles Act, which mandates that the Central Government may, by rules, provide for measures for the safety of children below four years of age, riding or being carried on a motor cycle.
7. Development of State-wise vehicle tracking platform in States / UTs (under Nirbhaya Framework): Ministry of Road Transport & Highways has approved a scheme (on 15th January, 2020) for implementation of “Development, Customization, Deployment and Management of State-wise vehicle tracking platform for Safety & Enforcement as per AIS 140 Specifications in States / UTs under Nirbhaya Framework” at total estimated cost of Rs. 463.90 Crore (including Central and State share, as per Nirbhaya Framework). MoRTH has received proposals from 30 States/UTs. It has released the funds amounting to Rs 192.95 Crore. So far, three States/UTs i.e. Himachal Pradesh, Puducherry and Bihar have commissioned the monitoring Centres a couple of months back and it is expected that more States/UTs are soon to follow the suit.
8. Safety Standards for Battery and related Components of Electric Vehicles: MoRTH has approved Amendment 3 to both AIS 156 and AIS 038 (Rev.2). AIS 156 is regarding Specific Requirements for L category [motor vehicles with less than four wheels, quadricyle] vehicles with electric power train and AIS 038 (Rev.2) is regarding Safety requirements with respect to the electric power train of M [motor vehicles with at least four wheels used for carrying passengers] and N [motor vehicle with at least four wheels used for carrying goods] category vehicles.
9. Fire Alarm System and Fire Protection System in buses: The Ministry, vide notification dated 27th January 2022, introduced the Fire Alarm System and Fire Protection System in the Passenger (or, Occupant) Compartment in buses through an amendment in the AIS (Automotive Industry Standard)-135 for Type III buses [‘Type III’ Vehicles are those designed and constructed for long distance passenger transport, for seated passengers] and School Buses.
10. Safety Requirements for Road Train: This Ministry, vide GSR 200(E) dated 14th March 2022 amended CMVR 1989 to insert new rule 125K, regarding Safety Requirements for Road Train.
11. Standards for Safety Glass: The Ministry has notified S.O. 1533(E) dated 31st March exempted all motor vehicles including agricultural tractor fitted with cabin, construction equipment vehicle fitted with cabin and combined harvester from the application of rule 100 of the said rules, up to the 31st March, 2023 and the manufacturer shall continue to comply with the provisions of rule 100 as existed on 31st March, 2021.
(ii) RELIEF MEASURES
1. Compensation to victims of hit and run accidents: Compensation to Victims of Hit and Run Motor Accidents Scheme: The Ministry has notified a new scheme for compensation of victims of Hit & Run motor accidents vide notification dated 25th February, 2022 to cater to enhanced compensation (from Rs 12,500 to Rs 50,000 for grievous hurt and from Rs 25,000 to Rs 2,00,000 for death).The process of application for compensation and the release of payment to victims has also been made time bound. This scheme will supersede the Solatium Scheme, 1989 from 1st April, 2022 onwards.
2. Accident report submission timeline: The Ministry issued notification dated 25 Feb 2022 to mandate the procedure for detailed investigation of road accidents, the Detailed Accident Report (DAR) and its reporting, along with timelines for different stakeholders, for quick settlements of claims by the Motor Accident Claim Tribunal (MACT). Further, it has mandated incorporation of validated mobile number in the Certificate of Insurance.
3. Motor Vehicle Accident Fund Rules: MoRTH has also published rules on 25.2.2022 regarding creation, operation, sources of fund etc. of the Motor Vehicles Accident Fund. This fund shall be used for providing compensation in case of Hit & Run Accident, treatment for accident victims and any other purpose, as may be specified by the Central Government.
Union Ministry of Road Transport & Highways conducted 1st Meeting of Consultative Committee of Members of Parliament attached to the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways on “Road Safety” on 24th March, 2022 to discuss various issues related to Road Safety.
G. LOGISTICS & ALLIED HIGHWAY INFRASTRUCTURE
1. MULTI MODAL LOGISTICS PARKS (MMLPs)
The Ministry finalized the Model Concessionaire Agreement (MCA) for the MMLPs to be developed under the Bharatmala Pariyojana in October 2021 through an elaborate process of inter-Ministerial consultations. The document serves as the Developer Agreements / Concession Agreements for the individual MMLP projects under the Pariyojana. In addition to the MCA, the Ministry, in November 2021, also finalized and approved the Model RFP document of selection of Concessionaire for development of MMLPs.
A network of 35 Multimodal Logistics Parks is planned to be developed as part of Bharatmala Pariyojana, with a total investment of about Rs 46,000 crore, which once operational, shall be able to handle around 700 million metric tonnes of cargo. Of this, MMLPs at 15 prioritized locations will be developed with a total investment of about Rs 22,000 Crore.
These Multi-Modal Logistics Parks shall serve as regional cargo aggregation and distribution hubs for various industrial and agricultural nodes, consumer hubs and EXIM gateways such as seaports with multi-modal connectivity. In certain cases, the MMLPs are also being developed in tandem with the Inland Waterway Terminals under the Sagarmala Pariyojana to further reduce the cost of inland cargo movement at a much larger scale as compared to conventional road-based movement.
(i) MMLP Jogighopa (Assam) in advanced stage: Out of 15, development of MMLP in Jogigopha (Assam) is in an advanced stage. The estimated cost of the first phase of the project is 793.97 crore. The foundation stone of the project was laid in October 2020 by Hon’ble Minister (RT&H) Shri Nitin Gadkari. This MMLP will serve as the distribution centre for all North-Eastern states and facilitate cross-border trade with Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal.
(ii) MMLP Chennai project awarded to Reliance; Bids for 3 MMLPs in process: In addition, MMLP Chennai project has also been awarded to Reliance Industries Limited. The estimated project cost is Rs 1424 crore. This is the first MMLP project which has been awarded under PPP mode. Bids for MMLP Bengaluru, MMLP Nagpur and MMLP Indore are in process. Work on Pre-feasibility study for remaining locations is in progress.
(iii) MoU for MMLP Jalna: In presence of Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways Shri Nitin Gadkari and Union Minister for Ports, Shipping and Waterways and Ayush Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, an MoU was signed between National Highways Logistics Management Limited (NHLML) & JNPT for the development of Multi Modal Logistics Park (MMLP) at Jalna in Maharashtra.
2. PORT CONNECTIVITY
India has a total of 226 ports which comprise 12 Major ports. At present, there are 87 operational / under implementation ports which are being considered for assessment in terms of connectivity or capacity augmentation. For improving first/ last mile connectivity to all Major & Non-major ports of the country specifically the operational/ under implementation ports, 55 port connectivity and associated hinterland projects with a total length of 2,779 km have already been initiated by the Ministry and its implementing agencies. As of now, 8 projects of length 294 km have been completed, 14 projects of length 1,645 km are under implementation, 13 projects of length 363 km are under bidding and 20 projects of length 476 km are yet to be awarded. Post completion of these projects, 45 maritime ports will be provided with National Highway or 4 Lane+ connectivity.
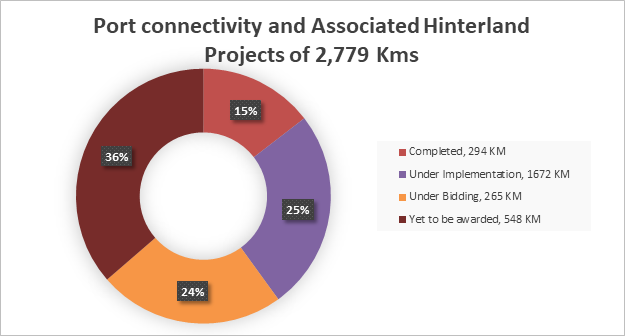
MoRTH is working to enhance the ports logistics ecosystem by connecting Major & Minor Ports with National Highways, with NHLML spearheading this endeavour. The programme has been envisioned to connect all major ports, non-major ports as well as inland waterway terminals in the country to create an integrated network to support efficient and unhindered freight movement. As many as 52 critical infrastructure gap projects identified by MoPSW for connecting maritime ports and IWTs (Inland Waterway Terminals) to be taken up under PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan. Currently, DPR of total 56 projects (including 11 IWT projects) under this category with total of 1215 km length are under bidding stage for the feasibility assessment of these projects, which is being carried out by NHAI.
3. WAY SIDE AMENITIES
To improve the comfort and convenience of the Highway users, the Ministry has planned the development of state-of-the-art Way Side Amenities (WSA) at about every 40 kms along the National Highways on PPP mode. These facilities are aimed to provide multiple options of rest and refreshment for the highway commuters during their journey. Some of the mandatory facilities being developed at each WSA are fuel stations, EV charging stations, food court / restaurants, dhabas, convenience stores, clean and hygienic toilet facilities, drinking water, first aid / medical room including child care room, dedicated area for promoting local artisans, car/bus/truck parking, drone landing facilities / helipad etc.
A total of 600+ sites are planned to be awarded by 2024-25 of which 144 Wayside Amenities (WSAs) have already been awarded. 72 WSAs are under bidding stage. These WSAs will offer huge opportunities for the investors, developers, operators and retailers. All upcoming Greenfield/Access Controlled Highway projects are provisioned to have Way Side Amenities essentially, which will also promote local economy by generating employment opportunities and help local people to market their unique produces/ handicrafts etc. at village haats developed at these places.
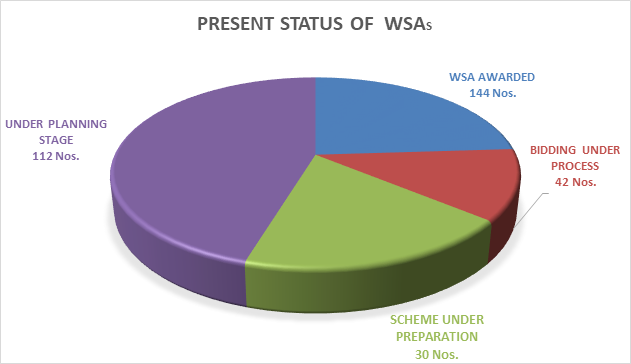
4. UTILITY CORRIDORS
Work has been awarded by laying of Optical Fibre Cable (OFC) project along Delhi-Mumbai Expressway and Bengaluru-Hyderabad Expressway. The process for engaging consultant for carrying out feasibility study-cum-PMC is on. Also, the policy for allotment of OFC is being finalized.
H. NEW TECHNOLOGY
1. Brainstorming meet on new technology: A brainstorming session was organized between the Minister RT&H and senior officials of MoRTH with road developers (Concessionaires and Contractors), who are using new technology for road construction, on 20th July 2022 at Taj Mahal Hotel, Man Singh Road, New Delhi on the following focus areas:
(i) Soil Stabilization Techniques;
(ii) Ultra High-Performance Concrete;
(iii) Pre-cast structures;
(iv) Re-cycling of construction material;
(v) Pre-fabricated Modular Steel Bridges;
(vi) Geosynthetic
2. Industrialised Pre-cast Concrete has the benefits of all-weather and fast construction, reliable quality & enhanced performance durability, aesthetics due to uniformity in appearance and minimum user time delay/reduced carbon emission/reduced noise & air pollution due to reduced construction activities at site, etc. To add to that, it will also play an integral role in accelerating the growth of the MSME sector. To harness the benefits of pre-fabrication in construction of National Highways, Expressways & Other Centrally Sponsored Road Projects, MoRTH has made mandatory to use factory manufactured pre-cast concrete elements in projects within 100 km radius of Pre-cast factory. The minimum mandatory usage should be 25% of total concrete volume other than the foundations & sub-structures of Bridges/Viaduct/RoB.
I. GREEN INITIATIVES
1. Hydrogen fuel cell EV launched: On 16th March, Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways Shri Nitin Gadkari launched the world’s most advanced technology – developed Green Hydrogen Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) Toyota Mirai. This is a first of its kind project in India which aims to create a Green Hydrogen based ecosystem in the country by creating awareness about the unique utility of Green Hydrogen and FCEV technology. It is an important initiative which will promote clean energy and environmental protection by reducing dependence on fossil fuels and thereby make India ‘Energy Self-reliant’ by 2047.
2. Hydrogen as an IC Engine Fuel in BS IV vehicles:- The Ministry vide draft GSR 683(E) dated 6th September, 2022 has notified the use of Hydrogen as an IC Engine Fuel in BS IV vehicles with Gross Vehicle Weight greater than 3.5 tonnes. Earlier, GSR 889(E) dated 16th Sept 2016 was notified to introduce Hydrogen as a Fuel for Vehicles with Gross Vehicle Weight less than or equal to 3.5 tonnes. Comments and suggestions have been invited from stakeholders within period of thirty days.
J. VEHICLE SCRAPPING POLICY
As a part of the forward-looking Budget 2021-22, the Government of India has introduced the Voluntary Vehicle-Fleet Modernization Program (V-VMP) or “Vehicle Scrapping Policy”, which is aimed at creating an eco-system for phasing out of unfit and polluting vehicles in an eco-friendly manner. The policy targets voluntary scrapping of unfit commercial and passenger vehicles, based on their fitness, irrespective of vehicle age.
MoRTH has envisaged a digital and user-friendly implementation of this policy. In this regard, the final rules for setting up automated fitness testing stations and registered vehicle scrapping facilities were issued by MoRTH on 23rd September 2021. These rules came into effect on 25th September 2021. The amendments to these rules have also been carried out through GSR Notification 695(E) dated 13.09.2022 which provides for amendments in Registration and Functions of Vehicle Scrapping Facility Rules, 2021 earlier published vide GSR 653(E) dated 23.09.2021 and through GSR notification 797(E) dated 31.10.2022 which provides for amendments in the rules for automated fitness testing earlier published vide G.S.R. 652(E) dated 23 September 2021.These rules have been kept very simple for the investors and have been prepared in consultations with industry and other stakeholders.
In order to attract private investment in the vehicle scrapping ecosystem, a single window system has been developed. This portal is part of the National Single Window System (NSWS), which is hosted by DPIIT and Invest India. Currently, 11 states have been onboarded onto NSWS for V-VMP – Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Assam, Goa, Uttarakhand, and Chandigarh. Expeditious onboarding of all other states/UTs on the NSWS has also been initiated.
(1) 117 applications under process: As on 14.11.22, applications of 117 investors are under process which have shown interest for RVSF out of which 36 applications have been approved by the respective State Governments (Bihar – 21, Gujarat – 3, Uttar Pradesh – 4, Haryana – 2, Madhya Pradesh – 2, Assam – 4). Similarly, 349 applications are under process for ATS, out of which 64 have been approved (Bihar – 48, Chhattisgarh – 8, Gujarat – 4, Uttarakhand – 2, Assam – 2). In addition, 84 ATSs across 11 states are proposed under the State/UT Government control through Requested for Proposal (RFP) by doing the necessary tendering.
(2) Investor summits: Investor summits have been conducted across 16 states to promote salient features of the V-VMP policy, attracting private investment by showcasing the Govt. of India as well as the State Government’s policies. As per projections based on vehicle registrations data on Vahan, 40-45 RVSFs are required to be set up in the next 2 years and 60-70 RVSFs in coming 5 years across India. Similarly, there is a requirement of 130-150 ATS in the next 2 years, and 450-500 ATS in coming 5 years across India.
K. INDIAN ACADEMY OF HIGHWAY ENGINEERS (IAHE)
1. Training Programme Conducted During 2022: During 2022, the Academy organized 14 In-campus training programmes which include first 10 months foundation training programme for Ministry`s Assistant Executive Engineers, three 16 weeks foundation training program for Deputy Managers of NHAI, two for Border Roads Organization and NHAI; two refresher courses for Ministry’s Senior Technical Officers, two Mandatory Training Programme on Preparation of DPR for Highway Projects for the personnel of Consultants, one course for National Quality Monitors of NRIDA and three 15 Days Certificate Courses for Road Safety Auditors; 37 online training programmes/workshop. In campus & online training programme total 2486 Engineers and Professionals participated.
Besides three courses were also conducted on “Avoidance of Collapses of Pre-stressed Concrete Elevated Structures & Bridges during Construction” one each at Surat (Gujarat), Indore (Madhya Pradesh) and Kolkata (West Bengal) in which 317 professionals participated. Three Mid-Career Training Programme — one for Chief Engineers (CEs) and two for Superintending Engineers of MoRTH — in which 35 Engineers of the Ministry participated. One Training Programme was also conducted on Executing Works of Bridges on EPC Mode sponsored by UPSBCL at Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh in which 57 Engineers participated.
2. Establishment of Centre for Advanced Transportation Technology & System (CATTS) in IAHE: MoRTH has sanctioned an estimate amounting to Rs 48.71 crore during 2019-20 (revised cost Rs 52.13 crore sanctioned during 2022-23) to undertake a project for capacity building, technology transfer and creation of an enabling environment for establishment of CATTS in IAHE in partnership with University of New South Wales (UNSW), Sydney and two premier Universities.
L. RECORDS / RECOGNITIONS
1. Adding jewel to the crown of records, India Book of Records have awarded certificates in respect of creation of record for Highest Quantity of Bituminous Mix laid for road construction in 100 Hrs. Longest Length of Flexible Pavement (DBM Course) road construction in 100 Hrs was awarded to PNC Infratech Ltd. This was achieved by PNC Infratech Ltd at the Construction of 8-Lane access-controlled expressway starting from junction with NH-47 near Bhamiya village and ending at junction with SH-175 in Baletiya village in Panchmahal district (Ch-780+920 to Ch-803+420. Design Ch-328+500 to Ch-351+000) section of Delhi-Vadodara Greenfield Alignment (NH-148N) in Gujarat.
2. Team Maharashtra Metro & Team NHAI on 10th July achieved the world record in Nagpur by constructing longest Double Decker Viaduct (3.14 KM) with Highway Flyover & Metro Rail Supported on single column piers.
3. NHAI has created a Guinness World Record for the longest continuously laid bituminous lane of 75 kilometers in 105 hours and 33 minutes on the national highway between Amravati and Akola districts in Maharashtra. The project was implemented by 720 workers including a team of independent consultants who worked day and night. The total length of the 75 kilometers of single-lane continuous bituminous concrete road is equivalent to 37.5 kilometers of two-lane paved shoulder road and the work started on June 3, at 7:27 am and was completed on June 7, at 5 pm. The previous Guinness World Record for the longest continuously laid bituminous was for building 25.275 kilometers of road which was achieved in Doha, Qatar in February 2019 and that task was completed in 10 days.




